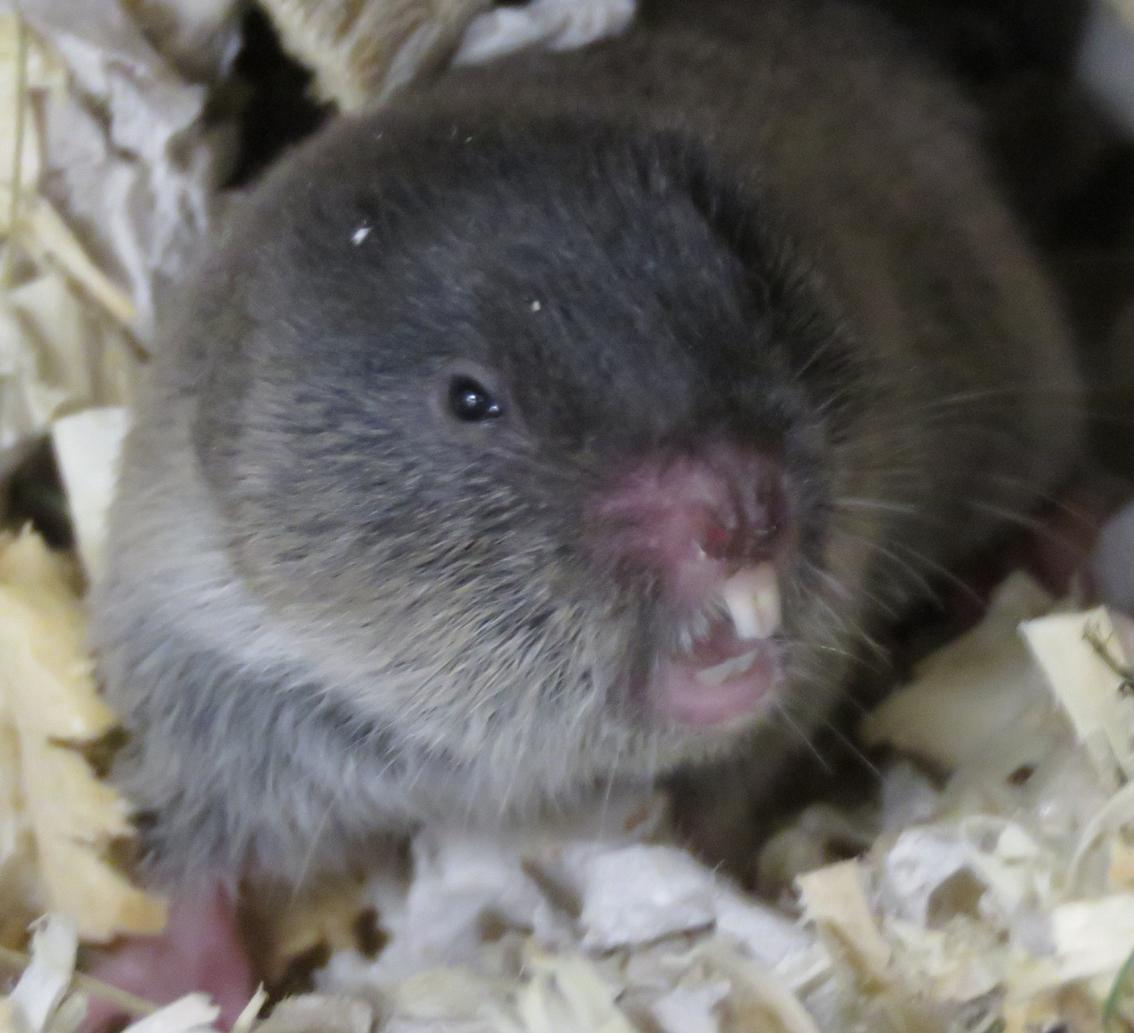

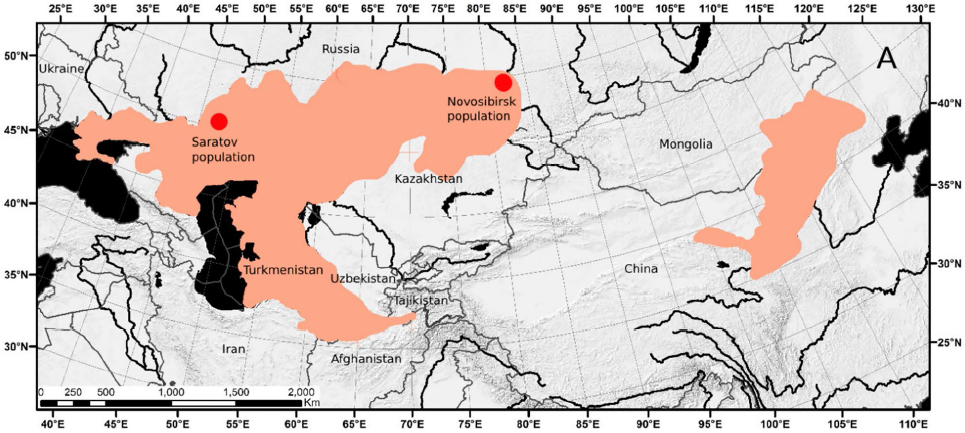
Subterranean rodents are of particular interest for population genetic studies. They are characterized by natural habitat fragmentation, limited dispersal, relatively low fecundity, and low population density. Researchers from St. Petersburg University, the Institute of Animal Taxonomy and Ecology of the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences (IAET SB RAS), and the A.N. Severtsov Institute of Ecology and Evolution of the Russian Academy of Sciences (IEE RAS) studied genetic diversity in two populations of the northern mole vole (Ellobius talpinus). One population was located in the center of the species' range in the Saratov Region, and the other was on the eastern periphery of its range in the Novosibirsk Region.
Analysis of both nuclear and mitochondrial markers revealed that all genetic diversity parameters were significantly lower at the periphery of the range. The polymorphism of the more genetically diverse Saratov population at microsatellite loci was close to the average for mammals as a whole, lower than that of the vast majority of non-subterranean vole species, and comparable to that of the other two subterranean vole species. Overall, this is consistent with the hypothesis of accelerated loss of genetic diversity in rodents with this ecological specialization. At the same time, genetic diversity of the mitochondrial marker in the Saratov population was quite high. This could be a consequence of secondary contact between several highly divergent subpopulations. Thus, these data clearly illustrate the pattern according to which the indices of mitochondrial haplotype diversity of terrestrial mammals have a U-shaped distribution: a large number of species with very low values (the result of long-term isolation) and a large number with high values (the result of mixing of mitochondrial subpopulations and/or immigration of males). Such a tendency towards a dichotomy of genetic diversity may be particularly characteristic of subterranean mammals.
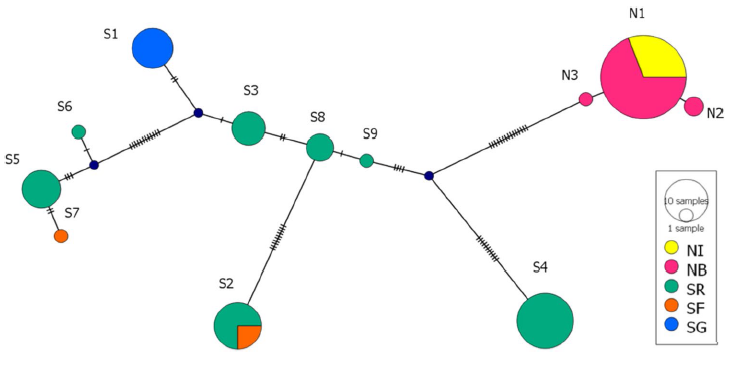
Fig.3: The network of mitochondrial D-loop haplotypes in the northern mole vole Ellobius talpinus, where shading along the lines indicates the number of mutations between haplotypes, and black circles between haplotypes correspond to intermediate haplotypes. S – Saratov, N – Novosibirsk
As expected for a subterranean species with limited dispersal capabilities, a high level of genetic differentiation was detected even over distances of several kilometers. Within-population genetic structure reflects dispersal strategies. Sexual differences in dispersal lead to differences in the structure and dynamics of nuclear and mitochondrial genes. In most mammalian species (including the vast majority of vole species and subterranean representatives from other taxa), the dispersing sex is male.
"The mole voles of the Novosibirsk population retain a typical vole dispersal pattern, whereas no sex differences in dispersal were detected in the Saratov population. This could be due to landscape and ecological features and different reproductive systems, such as the monopolization of reproduction by a single female within a family group in the Saratov region and polygynous reproduction in the Novosibirsk region," explained Elena Volodina, PhD, senior researcher at the Institute of Ecology and Evolution of the Russian Academy of Sciences.
The results of the study were published in the Q1 journal Mammalian Biology: Rudyk A.I., Kuprina K., Bergaliev A.M., Galkina S.A., Romanovich A.E., Novikov E.A., Volodina E.V., Smorkatcheva A.V. Genetic diversity and population structure of the subterranean rodent, northern mole vole (Ellobius talpinus). Mammalian Biology, 2025, v. 105, N 5, pp. 571-588.
